python plotly画两个y轴
使用 plotly 画图的时候,如果有两个指标的数值相差很大时,这时候需要y轴拆分成两个,这样能更清楚的看到两个指标的关系。
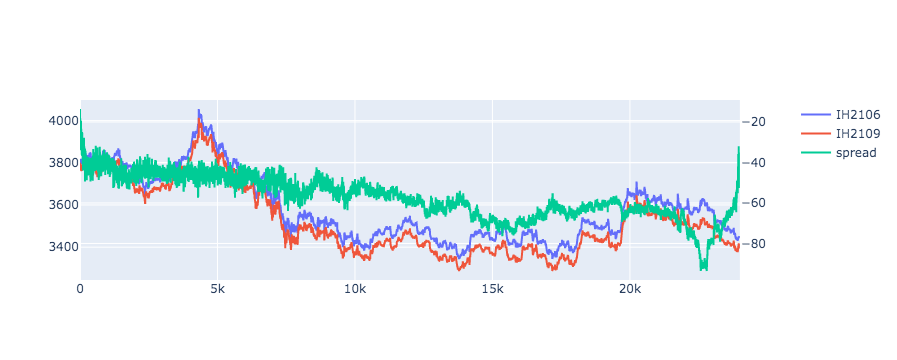
下面代码展示了跨期价差套利的图像。
1 | import plotly.graph_objects as go |
使用 plotly 画图的时候,如果有两个指标的数值相差很大时,这时候需要y轴拆分成两个,这样能更清楚的看到两个指标的关系。
下面代码展示了跨期价差套利的图像。

1 | import plotly.graph_objects as go |
通过pip安装软件,使用默认源的时候,往往下载速度很慢,所以需要配置到国内的源。
临时安装某个包。
1 | pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package |
设为默认配置:
1 | pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple |
会生成一个配置文件,在macOS下面的位置如下:
1 | ~/.config/pip/pip.conf |
内容为:
1 | [global] |
再更新pip本身:
1 | pip install pip -U # 更新pip |
临时使用某个镜像。
1 | pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple pip -U |
使用jupyter lab画图时,图片不显示而显示空白。
说一下目前最新版本的处理情况。
python base环境
1 | python 3.12.5 |
python env py310环境
1 | python 3.10.15 |
在py310环境中安装了plotly以后,执行代码时,可能会遇到如下错误:
1 | ValueError: Mime type rendering requires nbformat>=4.2.0 but it is not installed |
按提示安装nbformat,mamba install nbformat,重启Kernel。再次执行代码时,程序不报错了,但图形位置会显示为空白。
本来只需要在base环境再安装jupyterlab-plotly插件就行了,但会报错,提示版本不匹配。
所以解决方案,就是在base环境再安装一下相同版本号的plotly。安装好了以后,再查看插件jupyterlab-plotly,就已经同时安装成功了。
1 | $ jupyter labextension list |
这时,重新启动jupyter lab,plotly的图形就可以正常显示了。
如果要安装@jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager v5.0.13 enabled OK (python, jupyterlab_widgets),执行下面命令:
1 | mamba install ipywidgets |
首先要确保的是以下两个库jupyterlab和ipywidgets已经安装完成,并且版本”jupyterlab>=3” “ipywidgets>=7.6”。
需要安装一个扩展工具。一般来说,JupyterLab 3.x以上,会自动安装好,并且是安装在JupyterLab被安装的Python环境下面。
1 | $ jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager jupyterlab-plotly |
安装完可以查看一下。
1 | # Check that jupyterlab-plotly is installed |
这个工具需要依赖nodejs,如果没有安装的话,需要安装一下。
1 | $ mamba install nodejs |
重启jupyter lab,图片即可正常显示。
有几个点需要注意的是:
jupyterlab以及jupyterlab的extension是安装在server端的,但是plotly包是安装在其他python环境里面的。